

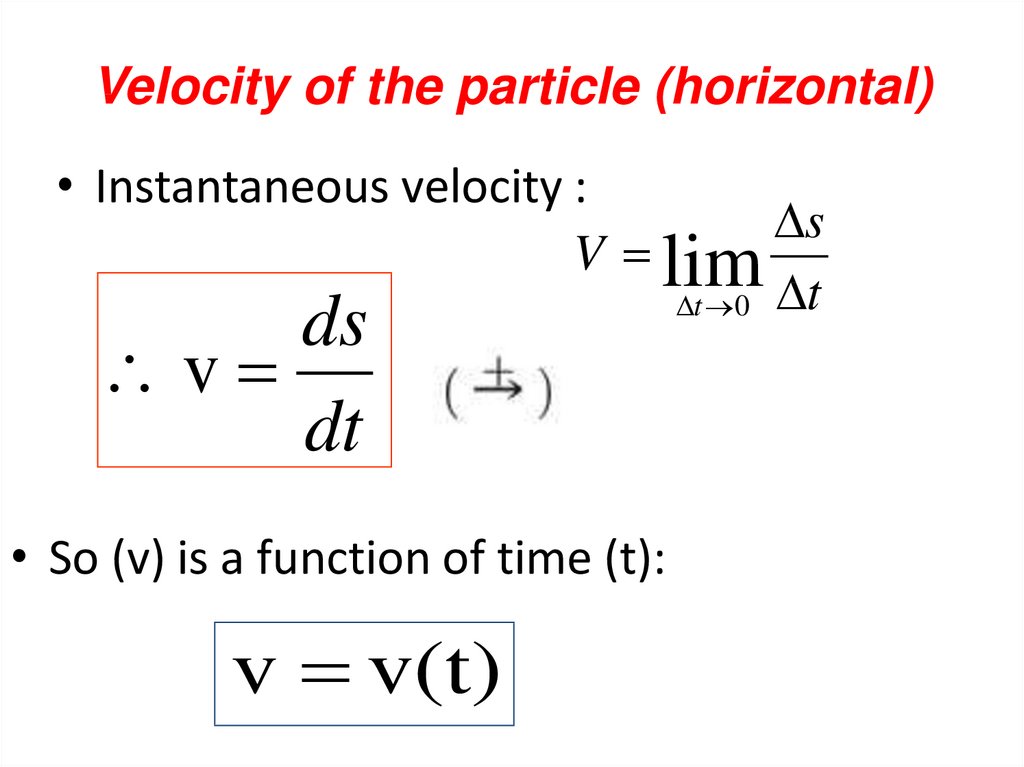
Acceleration aavg = Δv Δt a= dv dt d 2s a= dt a ds = v dv IN CASE.Min.INTRODUCTION Dynamics includes: - Kinematics Kinematics is used to relate displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time, without reference to the cause of the motion - Kinetics Kinetics is used to predict the motion caused by given forces or to determine the forces required to produce a given motion CHAPTER KINEMATICS OF PARTICLES §1.1 RECTILINEAR MOTION OF PARTICLES Position : r, s Displacement Δr = r '− r Δs = s ' − s Velocity: Δr Δt dr v = dt v avg = ds v = dt Introduction, Structure Types, Stability & Determinacy
The instructor reserves the right to make changes that may not be reflected in the handouts below, it is the students' responsibility to keep a complete and current set of notes for each lecture. The handouts highlight the lecture content and are by NO MEANS a complete set. Hibbeler, Prentice Hall, ISBN# 9767-2.ĭisclaimer: Students are expected to keep their own notes.

Elastic analysis of statically determinate beams, frames, and trusses deflections by the methods of virtual work and moment area influence lines for determinate structures modeling for structural analysis flexibility, stiffness, and approximate methods of analysis of indeterminate structures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
